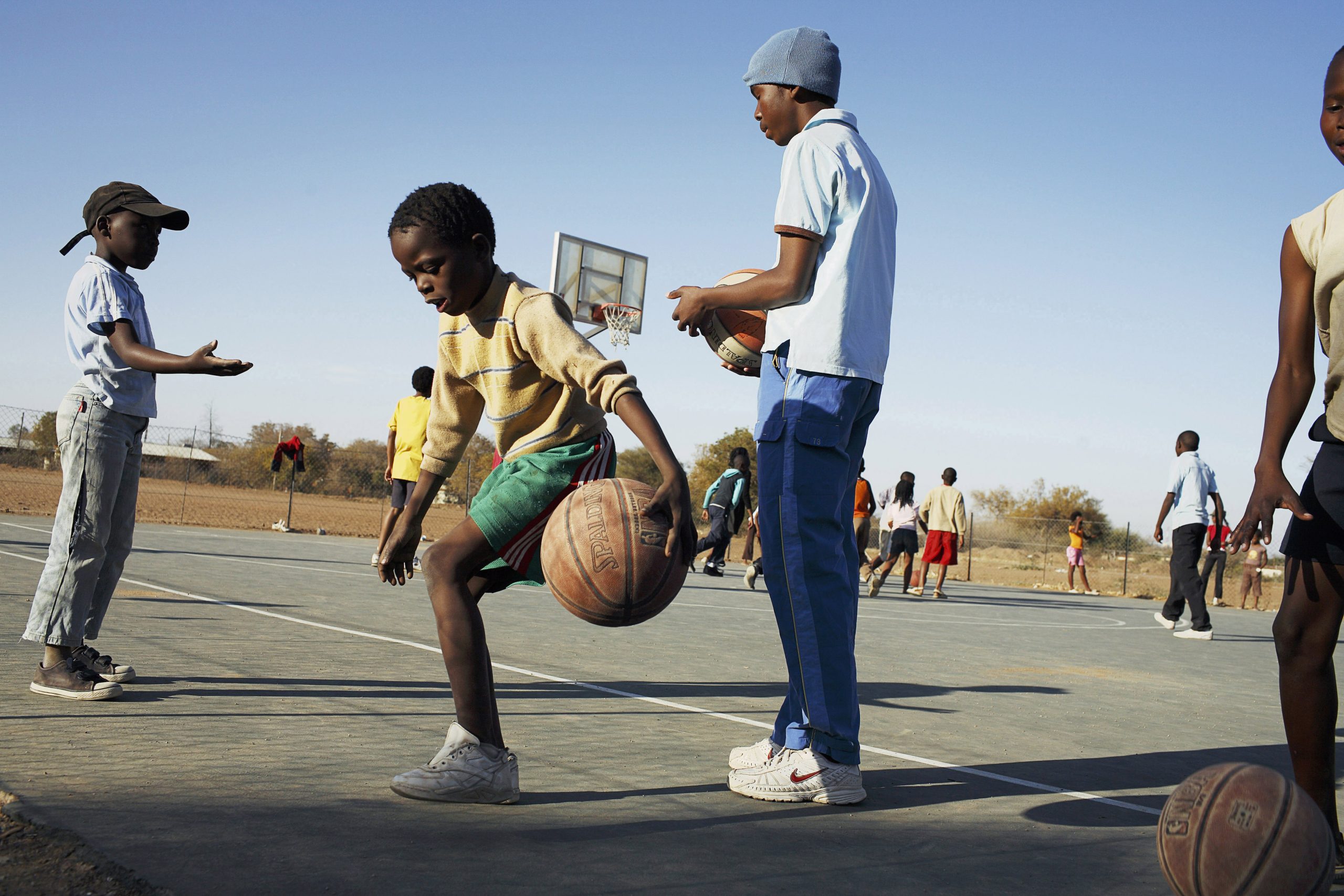
Botswana’s remarkable success in combating pediatric HIV/AIDS stands as a beacon of hope and a testament to the power of sustained public health initiatives. Once facing an existential threat from the virus, with a childhood infection rate among the world’s highest, Botswana has achieved a near-miraculous turnaround, slashing new pediatric infections by over 98 percent since the 1990s. This dramatic achievement offers crucial lessons for global health strategies and underscores the importance of comprehensive, long-term investment in healthcare infrastructure.
A Nation’s Fight Against a Pandemic:
At the height of the epidemic, Botswana faced a devastating reality. One in eight infants were born with HIV, leading to a nearly doubled mortality rate among young children. Thousands perished annually from AIDS, and a significant portion of the nation’s children lived with the long-term debilitating effects of the virus. The sheer scale of the crisis threatened the very fabric of Botswanan society. The situation was so dire that some observers spoke of a nation at risk of extinction due to the pandemic. However, the government, in collaboration with international organizations and healthcare professionals, embarked on an ambitious and multifaceted strategy to combat the epidemic.
The Keys to Success: A Multi-Pronged Approach:
Botswana’s triumph wasn’t achieved through a single intervention, but rather through a comprehensive and sustained effort encompassing several key strategies. Widespread access to antiretroviral treatment (ART) proved pivotal in preventing mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of HIV. This involved not only providing ART to pregnant women but also ensuring consistent adherence to treatment regimens. Moreover, the country invested heavily in comprehensive HIV testing programs, allowing for early diagnosis and timely intervention. This rapid identification of infected individuals enabled prompt treatment and prevented further transmission. Finally, sustained investment in healthcare infrastructure, including training healthcare professionals and bolstering the healthcare system’s capacity, was essential to maintaining the effectiveness of these programs.
Lessons Learned and Global Implications:
Botswana’s experience offers valuable insights for other nations grappling with HIV/AIDS. The success demonstrates the critical role of strong political commitment, sustained funding, and a comprehensive approach that integrates prevention, testing, and treatment. The nation’s proactive approach to addressing the crisis serves as a powerful example of how determined action can dramatically alter the course of a devastating pandemic. The lessons learned in Botswana highlight the importance of investing in healthcare infrastructure, training healthcare workers, and ensuring equitable access to essential healthcare services. This success story provides a blueprint for other countries battling similar challenges, offering hope and inspiration in the global fight against HIV/AIDS.
Conclusion:
Botswana’s remarkable achievement in reducing pediatric HIV infections to near-zero is a testament to the power of sustained commitment, comprehensive strategies, and collaborative efforts. This success story stands as a powerful example of what is possible when governments, healthcare professionals, and international organizations work together to tackle a global health crisis. The lessons learned from Botswana’s journey are crucial for shaping global health policy and forging a path towards a future free from the devastating impact of HIV/AIDS.
Based on materials: Vox