Supreme Court Poised to Weaken Voting Rights Act Protections
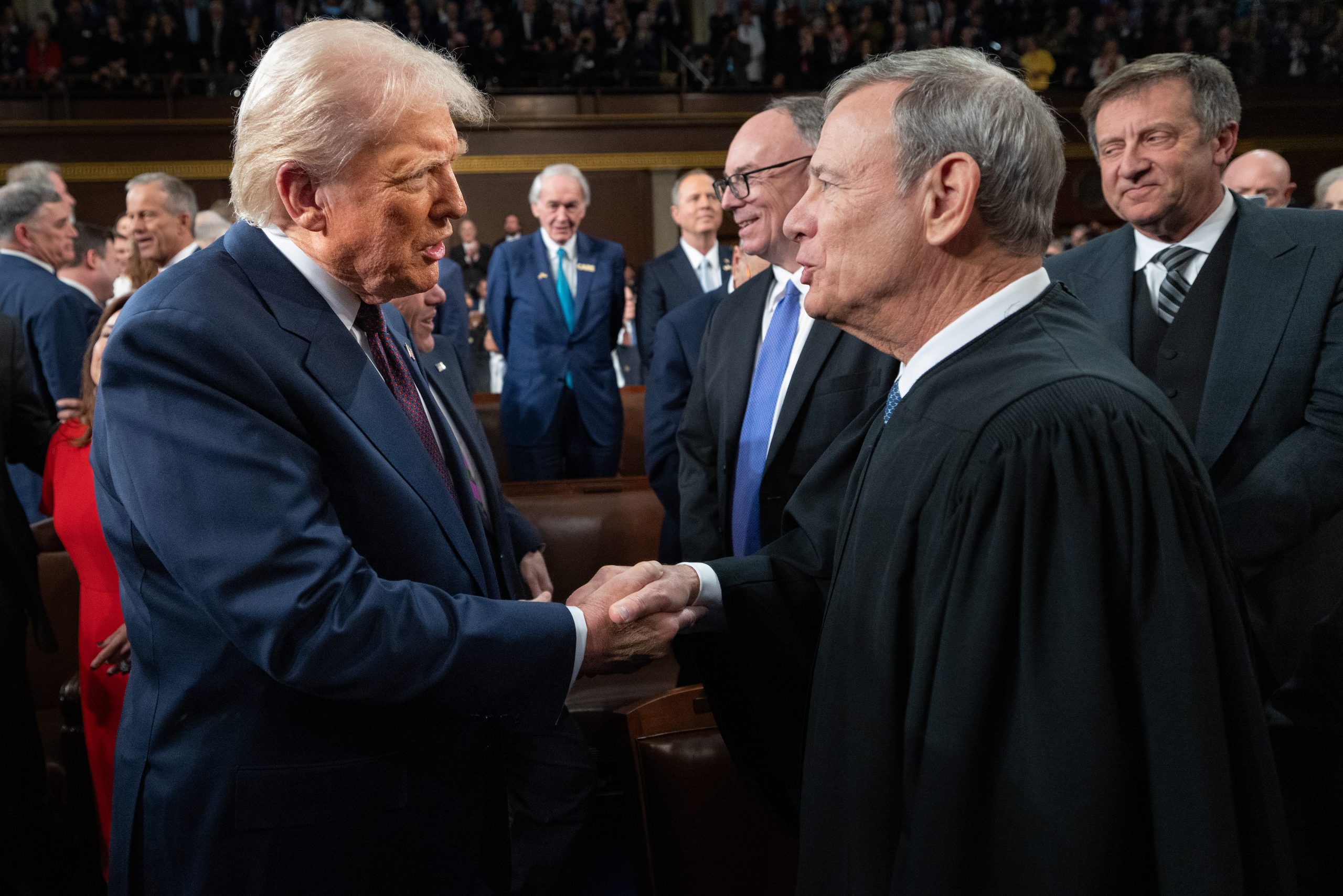
The future of the Voting Rights Act (VRA) hangs in the balance as the Supreme Court appears sharply divided along ideological lines over a case challenging safeguards against racially gerrymandered legislative maps. During oral arguments in
Louisiana v. Callais
, the justices grappled with the scope and application of the VRA, revealing deep disagreements about the legal standards for assessing claims of racial discrimination in redistricting.
A Partisan Divide on the Bench
The arguments made before the court made one fact clear: a partisan split is all but guaranteed. All six Republican-appointed justices seemed prepared to weaken or eliminate key provisions of the VRA that restrict racial gerrymandering. Meanwhile, the three Democrat-appointed justices appeared ready to uphold these protections. This ideological divide raises serious concerns about the future of voting rights in the United States, as a ruling against the VRA could open the door to more discriminatory voting practices.
Divergent Theories Among Conservative Justices
While the conservative justices seemed united in their desire to limit the VRA, they struggled to find common ground on the legal rationale for doing so. Justice Samuel Alito, for example, appeared to suggest that maps that exclude Black voters are acceptable if the exclusion was not the explicit purpose of the map. This argument raises concerns that discriminatory voting practices could be justified as long as they are cloaked in neutral language.
The lack of consensus among the conservative justices about how to justify weakening the VRA suggests that the court may struggle to produce a clear and coherent ruling. This uncertainty could lead to further litigation and confusion about the scope of the VRA, making it more difficult to protect voting rights in the future.
Implications for Future Elections
A Supreme Court ruling that weakens the VRA could have profound implications for future elections. Without strong federal protections against racial gerrymandering, states could be free to draw legislative maps that dilute the voting power of minority communities. This could lead to less representative government and further entrench existing inequalities.
The potential weakening of the VRA comes at a time when voting rights are already under attack in many states. The court’s decision in
Louisiana v. Callais
could embolden efforts to restrict voting access and further disenfranchise marginalized communities.
CONCLUSION:
The Supreme Court’s consideration of
Louisiana v. Callais
underscores the ongoing debate over the role of the federal government in protecting voting rights. With the court poised to weaken the VRA, the future of voting rights in the United States remains uncertain. The case highlights the importance of continued vigilance and advocacy to ensure that all citizens have equal access to the ballot box.
Based on materials: Vox