Supreme Court Hears Arguments on Trump’s National Guard Authority
The Supreme Court is currently grappling with a pivotal case,
Trump v. Illinois
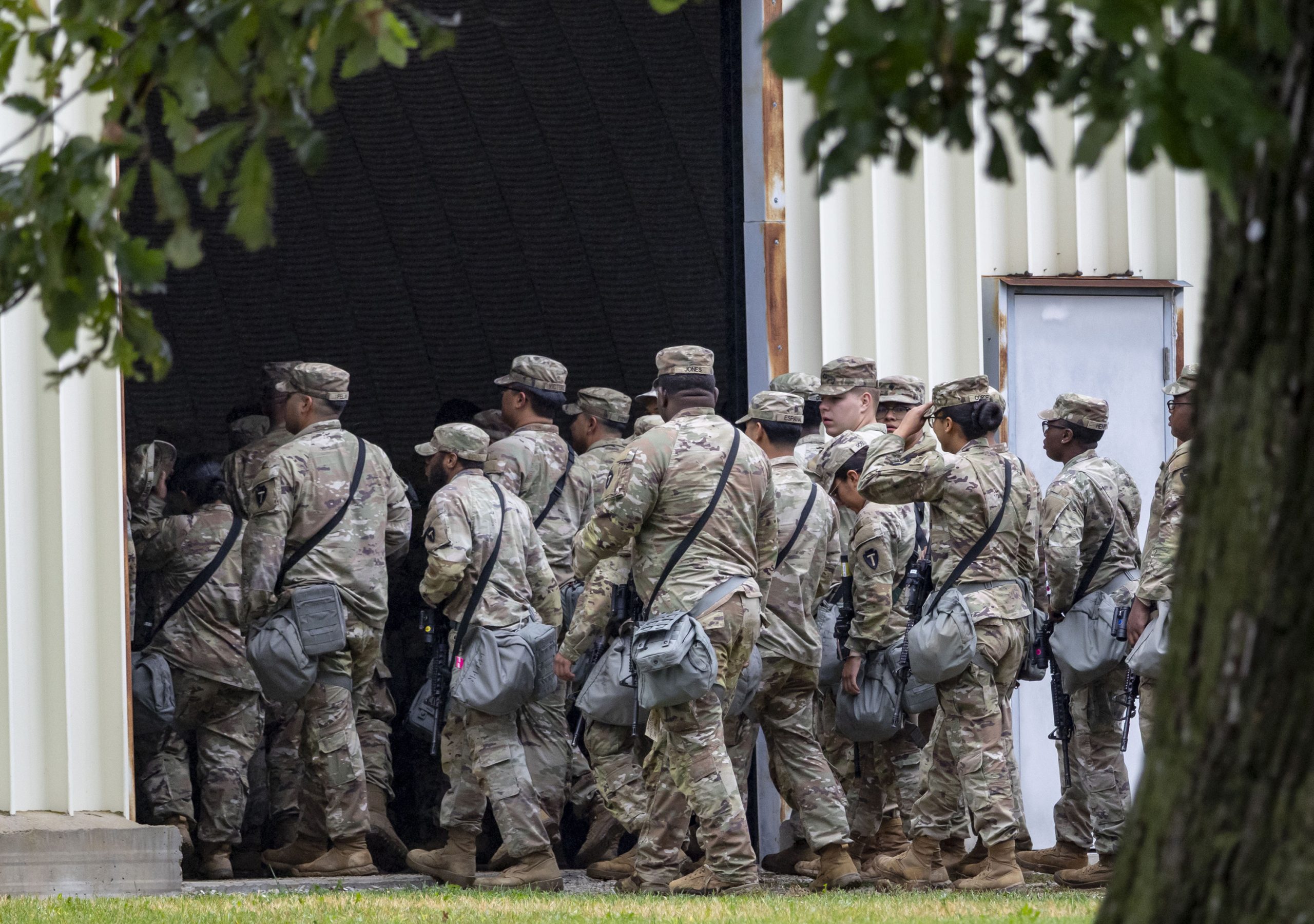
, that could significantly reshape the balance of power between the executive branch and state governments regarding the National Guard. At the heart of the matter is President Trump’s attempt to deploy federalized National Guard troops to quell protests near an immigration detention facility in Illinois. This move was previously blocked by two lower federal courts, which ruled that existing federal law doesn’t grant the president such authority.
The Core of the Dispute: Federal vs. State Control
The legal battle hinges on the interpretation of presidential powers concerning the National Guard. Traditionally, the National Guard operates under the command of state governors. However, the President can federalize these troops under certain circumstances, placing them under federal control. Trump’s legal team argues that the decision of when to exercise this power rests “exclusively” with the president and is beyond the purview of judicial review. This assertion raises fundamental questions about the checks and balances that define American democracy.
Implications for Presidential Power and Civil Unrest
The implications of this case extend far beyond a single protest in Illinois. A ruling in favor of Trump could establish a precedent allowing future presidents to deploy the National Guard for a wide range of domestic purposes, potentially including suppressing dissent or enforcing federal policies, even against the wishes of state governments. Critics fear this could lead to the militarization of domestic law enforcement and erode the traditional role of the National Guard as a force primarily under state control. The case also underscores the growing tension between federal authority and states’ rights, a recurring theme in American political history.
Conclusion: A Defining Moment for Federalism
The Supreme Court’s decision in
Trump v. Illinois
promises to be a landmark ruling, shaping the future of presidential power and the relationship between the federal government and the states. With a conservative-leaning court, the potential for a ruling that expands executive authority is significant. Regardless of the outcome, this case serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing debate surrounding the appropriate limits of presidential power and the importance of safeguarding the principles of federalism in a rapidly changing political landscape.
Based on materials: Vox